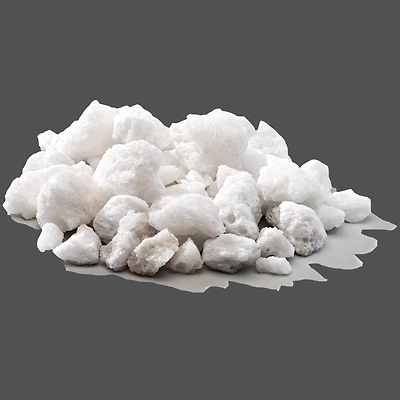
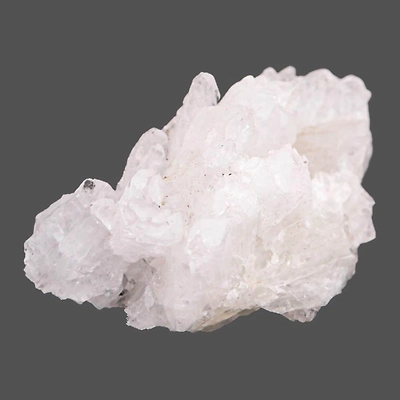
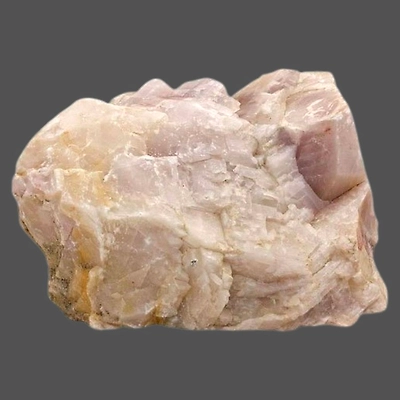
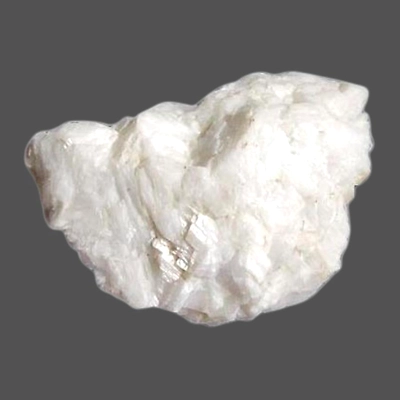
Alumina
Alumina is found in the regions of Odisha, West Bengal, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
There are several physical properties of alumina. It is high in hardness with the value of 9 on Mohs scale. It has sharp-edged grains, a high load bearing capacity, strong shock resistance, and thermal and chemical stability, besides their superior hardness.
Ball Clay
Ball clays are kaolinitic sedimentary clays that commonly consist of 20–80% kaolinite, 10–25% mica,
6–65% quartz.
CMC
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) or cellulose gum is a cellulose derivative with carboxymethyl groups (-CH2-COOH) bound to some of the hydroxyl groups of the glucopyranose monomers that make up the cellulose backbone.
Calcite
Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone.
Dolomite
Sodium triphosphate (STP), also sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP), or tripolyphosphate (TPP), is an inorganic compound with formula Na5P3O10.
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2.
STPP
Sodium triphosphate (STP), also sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP), or tripolyphosphate (TPP), is an inorganic compound with formula Na5P3O10.
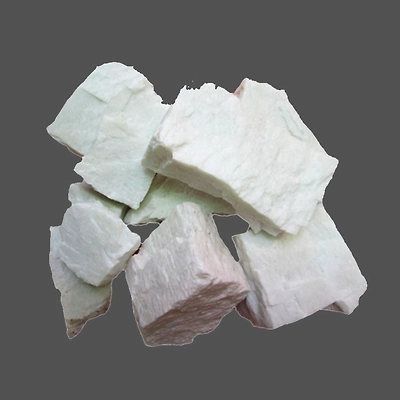
Talc Powder
Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral, composed of hydrated magnesium silicate with the chemical formula Mg₃Si₄O₁₀(OH)₂
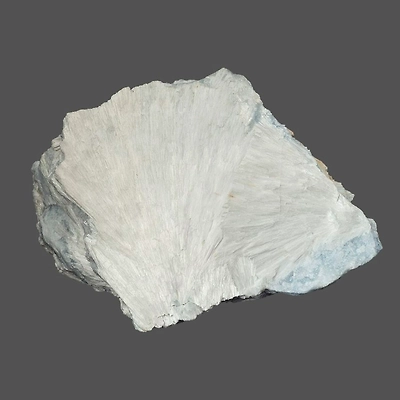
Wollastonite
Wollastonite is a calcium inosilicate mineral (CaSiO3) that may contain small amounts of iron, magnesium, and manganese substituting for calcium.
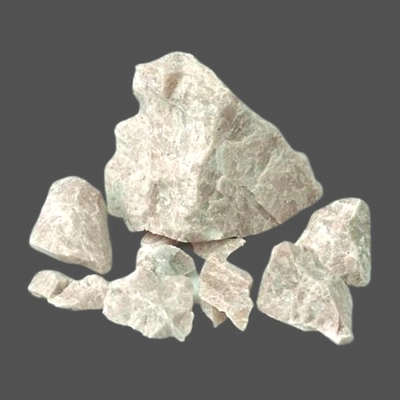
White Soda Feldspar
A feldspar is typically referred to as 'potash' if there is significantly more potassium than sodium
(typically there will be 2-5% Na2O).
White Potash Feldspar
A feldspar is typically referred to as 'potash' if there is significantly more potassium than sodium
(typically there will be 2-5% Na2O).